Content types
Content types are a way to define the structure of your content. Each content type can have its own set of fields.
Changing the default content type
If you want to change the default content type, open your frontmatter.json and write an entry for
the frontMatter.taxonomy.contentTypes setting. Visual Studio Code will automatically autocomplete
it with the default content type fields.
If in some case it wouldn't do this, here is the default content type structure:
"frontMatter.taxonomy.contentTypes": [
{
"name": "default",
"previewPath": null,
"pageBundle": false,
"fields": [
{
"title": "Title",
"name": "title",
"type": "string"
},
{
"title": "Description",
"name": "description",
"type": "string"
},
{
"title": "Publishing date",
"name": "date",
"type": "datetime",
"default": "{{now}}",
"isPublishDate": true
},
{
"title": "Article preview",
"name": "preview",
"type": "image"
},
{
"title": "Is in draft",
"name": "draft",
"type": "draft"
},
{
"title": "Tags",
"name": "tags",
"type": "tags"
},
{
"title": "Categories",
"name": "categories",
"type": "categories"
}
]
}
]Adapt the fields to your needs. For our documentation it looks as follows:
"frontMatter.taxonomy.contentTypes": [
{
"name": "default",
"previewPath": null,
"pageBundle": false,
"fields": [
{
"title": "Title",
"name": "title",
"type": "string"
},
{
"title": "Description",
"name": "description",
"type": "string"
},
{
"title": "Publishing date",
"name": "date",
"type": "datetime",
"default": "{{now}}",
"isPublishDate": true
},
{
"title": "Last modified date",
"name": "lastmod",
"type": "datetime",
"isModifiedDate": true
},
{
"title": "Navigation weight",
"name": "weight",
"type": "number"
}
]
}
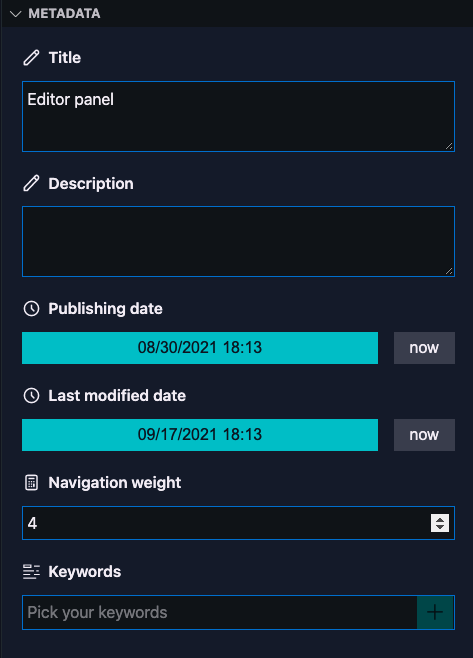
]The metadata section on the editor panel will render the following fields:
Content type properties
For the content type you can configure the following properties:
| Property | Type | Description | Default value |
|---|---|---|---|
name | string | Name of the content type | "" |
clearEmpty | boolean | Clears the fields from the front matter section if empty | false |
defaultFileName | string | Default file name to use when creating new content | index |
fields | array | Check the supported field types | [] |
filePrefix | string | Defines a prefix for the file name | null |
fileType | Enum: md, mdx, markdown, <your choice> | File type of for the content type you define. The type will be used to create the file when creating content. | md |
pageBundle | boolean | If set to true, the content will be created as a page bundle (folder) | false |
postScript | string | An optional post script that can be used after new content creation. In order to use this, you will have to set the value to the ID of your content script | null |
previewPath | string | Defines a custom preview path for the content type. When the preview path is not set, the value from the frontMatter.preview.pathName setting will be used | null |
template | string | Specify a path to a template file that will be used when creating new content with the content type | null |
allowAsSubContent | boolean | Allow the content type to be used as sub-content | false |
isSubContent | boolean | Defines the content type as sub-content | false |
slugTemplate | boolean | Defines the template for the slug | {{title}} |
Define your own type
In most cases, you'll work with multiple types of content where each type will have its defined set
of fields. If this is the case for your website, you'll need to add another content type to the
frontMatter.taxonomy.contentTypes setting.
Instead of overriding the default content type, you can also define a new content type. It requires
you to specify the name and fields.
ImportantThe
nameproperty value needs to be equal to thetypevalue you set in your Markdown front matter. You best define it via a template so that it's always defined. A default template will be available when initializing Front Matter in your project in the.frontmatter/templatesfolder.
Sample:
"frontMatter.taxonomy.contentTypes": [
{
"name": "default",
"fields": [
...
]
},
{
"name": "documentation",
"fields": [
...
]
}
]In the sample, documentation is used as the content type name. This means that in your article,
you'll need to add the type: documentation to your front matter to let the editor panel understand
which fields to show.
---
title: Content Types
slug: content-types
description: null
date: "2021-09-17T07:36:26.654Z"
lastmod: "2019-08-22T15:20:28.000Z"
weight: 4
type: documentation
---FieldsCheck out the fields section to learn which fields are supported.
Creating sub-content
By default, when you create new content, it will always be created in one of your defined folders
in the frontMatter.content.pageFolders setting.
In some cases, you want to create a hierarchy of content. For example, you want to create a
documentation site, where each topic has its own folder. The starting point is a page bundle which
contains the index.md file and all the related topics are created as separate files in the same
folder.
To support this, you can now make use of the allowAsSubContent and isSubContent properties on
your content type.
Allow as sub-content
The allowAsSubContent property is intended to be used for content types with a page bundle
(pageBundle: true). When you set this property to true, during the content creation, you will be
able to choose if you want to create content as parent or sub-content.
{
"frontMatter.taxonomy.contentTypes": [
{
"name": "parent",
"pageBundle": true,
"allowAsSubContent": true,
"fields": [
...
]
}
]
}Is sub-content
The isSubContent property is intended to be used for content types which will always be created as
sub-content. When you set this property to true, during the content creation, you be able to
select the parent folder.
{
"frontMatter.taxonomy.contentTypes": [
{
"name": "child",
"pageBundle": true,
"isSubContent": true,
"fields": [
...
]
}
]
}Using a template with the content type
When creating content that requires a pre-defined structure, you can use the template property.
The template property allows you to link a template file. On content creation, the contents of the
template file will be used to create the new content.
You can use the template property on any of your content types, even on the default content type
from Front Matter.
{
"frontMatter.taxonomy.contentTypes": [
{
"name": "default",
"pageBundle": false,
"template": "[[workspace]]/.frontmatter/templates/article.md",
"fields": [...]
}
}Run a script after your content is created
To run a custom script after your content is created, you can use the postScript property. The
postScript property allows you to link a script file by referencing its id. The script will be
executed after the content is created which gives you access to the whole front matter object.
{
"frontMatter.taxonomy.contentTypes": [
{
"name": "default",
"pageBundle": false,
"template": "[[workspace]]/.frontmatter/templates/article.md",
"fields": [...],
"postScript": "generate-social-image"
}
]
}In your custom script setting, you need to make sure that this script is available:
{
"frontMatter.custom.scripts": [
{
"id": "generate-social-image",
"title": "Generate social image",
"script": "./scripts/social-img.js"
}
]
}InfoMore information about custom scripts can be found in the custom actions section.
Link to content folders
In case you want to make sure that a content type is only available for specific folders,
you can use the contentTypes property on the frontMatter.content.pageFolders setting.
{
"frontMatter.content.pageFolders": [
{
"title": "Documentation",
"path": "[[workspace]]/content/docs",
"contentTypes": ["documentation"]
}
]
}Feedback/comments
Did you spot an issue in our documentation, or want to contribute? Edit this page on Github!